React 源码学习(七):生命周期
阅读源码成了今年的学习目标之一,在选择 Vue 和 React 之间,我想先阅读 React 。
在考虑到读哪个版本的时候,我想先接触到源码早期的思想可能会更轻松一些,最终我选择阅读0.3-stable。
那么接下来,我将从几个方面来解读这个版本的源码。
- React 源码学习(一):HTML 元素渲染
- React 源码学习(二):HTML 子元素渲染
- React 源码学习(三):CSS 样式及 DOM 属性
- React 源码学习(四):事务机制
- React 源码学习(五):事件机制
- React 源码学习(六):组件渲染
- React 源码学习(七):生命周期
- React 源码学习(八):组件更新
- React 源码学习(九):“脱胎换骨”
- React 源码学习(十):Fiber
- React 源码学习(十一):Scheduling
- React 源码学习(十二):Reconciliation
那么关于生命周期, React 当中生命周期有 2 个。
一个是组件的生命周期 _lifeCycleState ,另一个是复合生命周期 _compositeLifeCycleState 用于复合组件。
组件生命周期
那么关于组件的生命周期:
// core/ReactComponent.js
/**
* Every React component is in one of these life cycles.
*/
var ComponentLifeCycle = keyMirror({
/**
* Mounted components have a DOM node representation and are capable of
* receiving new props.
*/
// 已挂载
MOUNTED: null,
/**
* Unmounted components are inactive and cannot receive new props.
*/
// 未挂载
UNMOUNTED: null
});那么我们来观测到, ReactComponent 和 ReactCompositeComponent 关于 ComponentLifeCycle 的状态变化:
// core/ReactComponent.js
var ReactComponent = {
Mixin: {
getDOMNode: function() {
// 获取 DOM 节点时,组件必须为已挂载
invariant(
this._lifeCycleState === ComponentLifeCycle.MOUNTED,
'getDOMNode(): A component must be mounted to have a DOM node.'
);
},
construct: function(initialProps, children) {
// All components start unmounted.
// 实例化时,组件为未挂载
this._lifeCycleState = ComponentLifeCycle.UNMOUNTED;
},
mountComponent: function(rootID, transaction) {
// 挂载组件前检查组件应为未挂载
invariant(
this._lifeCycleState === ComponentLifeCycle.UNMOUNTED,
'mountComponent(%s, ...): Can only mount an unmounted component.',
rootID
);
// 挂载完后更新组件生命周期状态
this._lifeCycleState = ComponentLifeCycle.MOUNTED;
// Effectively: return '';
},
unmountComponent: function() {
// 卸载前检查组件应为已挂载
invariant(
this._lifeCycleState === ComponentLifeCycle.MOUNTED,
'unmountComponent(): Can only unmount a mounted component.'
);
// 卸载完后更新组件生命周期状态
this._lifeCycleState = ComponentLifeCycle.UNMOUNTED;
},
receiveProps: function(nextProps, transaction) {
// 更新 props 时,组件生命周期应为已挂载
invariant(
this._lifeCycleState === ComponentLifeCycle.MOUNTED,
'receiveProps(...): Can only update a mounted component.'
);
},
}
};// core/ReactCompositeComponent.js
var ReactCompositeComponentMixin = {
mountComponent: function(rootID, transaction) {
ReactComponent.Mixin.mountComponent.call(this, rootID, transaction);
// Unset `this._lifeCycleState` until after this method is finished.
this._lifeCycleState = ReactComponent.LifeCycle.UNMOUNTED;
// ...
this._lifeCycleState = ReactComponent.LifeCycle.MOUNTED;
},
replaceState: function(completeState) {
var compositeLifeCycleState = this._compositeLifeCycleState;
// 更新 state 时,组件生命周期必须为已挂载,或者复合组件生命周期为挂载中
invariant(
this._lifeCycleState === ReactComponent.LifeCycle.MOUNTED ||
compositeLifeCycleState === CompositeLifeCycle.MOUNTING,
'replaceState(...): Can only update a mounted (or mounting) component.'
);
},
_bindAutoBindMethod: function(method) {
function autoBound(a, b, c, d, e, tooMany) {
// 使用绑定上下文的方法时,组件生命周期必须为已挂载
if (component._lifeCycleState === ReactComponent.LifeCycle.MOUNTED) {
return method.call(component, a, b, c, d, e);
}
}
}
};复合组件生命周期
那么接下来,我们来看看复合生命周期以及其状态变化:
// core/ReactCompositeComponent.js
/**
* `ReactCompositeComponent` maintains an auxiliary life cycle state in
* `this._compositeLifeCycleState` (which can be null).
*
* This is different from the life cycle state maintained by `ReactComponent` in
* `this._lifeCycleState`.
*/
var CompositeLifeCycle = keyMirror({
/**
* Components in the process of being mounted respond to state changes
* differently.
*/
// 挂载中
MOUNTING: null,
/**
* Components in the process of being unmounted are guarded against state
* changes.
*/
// 卸载中
UNMOUNTING: null,
/**
* Components that are mounted and receiving new props respond to state
* changes differently.
*/
// 更新 props
RECEIVING_PROPS: null,
/**
* Components that are mounted and receiving new state are guarded against
* additional state changes.
*/
// 更新 state
RECEIVING_STATE: null
});
var ReactCompositeComponentMixin = {
construct: function(initialProps, children) {
// 实例化时置空复合生命周期
this._compositeLifeCycleState = null;
},
mountComponent: function(rootID, transaction) {
// 挂载前设置复合生命周期为挂载中
this._compositeLifeCycleState = CompositeLifeCycle.MOUNTING;
// 挂载完成后置空复合生命周期
// Done with mounting, `setState` will now trigger UI changes.
this._compositeLifeCycleState = null;
},
unmountComponent: function() {
// 卸载开始时设置复合生命周期为卸载中
this._compositeLifeCycleState = CompositeLifeCycle.UNMOUNTING;
if (this.componentWillUnmount) {
this.componentWillUnmount();
}
// 经过生命周期函数 componentWillUnmount 后,置空复合生命周期
this._compositeLifeCycleState = null;
},
receiveProps: function(nextProps, transaction) {
// 更新 props 时设置复合生命周期为更新 props
this._compositeLifeCycleState = CompositeLifeCycle.RECEIVING_PROPS;
if (this.componentWillReceiveProps) {
this.componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps, transaction);
}
// 执行生命周期函数 componentWillReceiveProps 后,设置复合生命周期为更新 state
this._compositeLifeCycleState = CompositeLifeCycle.RECEIVING_STATE;
// ...
// 操作 state 更新相关后,置空复合生命周期
this._compositeLifeCycleState = null;
},
replaceState: function(completeState) {
// 更新 state
var compositeLifeCycleState = this._compositeLifeCycleState;
// 仅限生命周期为挂载中或者复合生命周期为挂载中可以更新 state
invariant(
this._lifeCycleState === ReactComponent.LifeCycle.MOUNTED ||
compositeLifeCycleState === CompositeLifeCycle.MOUNTING,
'replaceState(...): Can only update a mounted (or mounting) component.'
);
// 仅限复合生命周期不为更新 state 或者不为卸载中
invariant(
compositeLifeCycleState !== CompositeLifeCycle.RECEIVING_STATE &&
compositeLifeCycleState !== CompositeLifeCycle.UNMOUNTING,
'replaceState(...): Cannot update while unmounting component or during ' +
'an existing state transition (such as within `render`).'
);
this._pendingState = completeState;
// Do not trigger a state transition if we are in the middle of mounting or
// receiving props because both of those will already be doing this.
// 如果我们正在安装或接收道具,请不要触发状态转换,因为这两个道具都已经在进行此操作了。
// 仅限复合生命周期不为挂载中 或者不为更新 props
if (compositeLifeCycleState !== CompositeLifeCycle.MOUNTING &&
compositeLifeCycleState !== CompositeLifeCycle.RECEIVING_PROPS) {
// 更新复合生命周期为更新 state
this._compositeLifeCycleState = CompositeLifeCycle.RECEIVING_STATE;
// ... 执行更新相关操作
// 置空复合生命周期
this._compositeLifeCycleState = null;
}
},
};生命周期函数方法
那么到此,实现生命周期功能。那么让我们来看看那些生命周期的钩子都在哪里:
// core/ReactCompositeComponent.js
var ReactCompositeComponentInterface = {
mixins: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_MANY,
props: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_ONCE,
getInitialState: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_ONCE,
render: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_ONCE,
// ==== Delegate methods ====
// **一下内容为 Google 翻译**
// 最初创建组件并即将安装时调用。 这可能有副作用,但必须在 `componentWillUnmount` 中清除此方法创建的任何外部订阅或数据。
componentWillMount: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_MANY,
// 在组件已装入并具有DOM表示形式时调用。 但是,无法保证DOM节点位于文档中。 在第一次装入(初始化和渲染)组件时,将此作为操作DOM的机会。
componentDidMount: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_MANY,
// 在组件接收新道具之前调用。 使用此作为通过使用 `this.setState` 更新状态来对prop转换作出反应的机会。 目前的道具是通过 `this.props` 访问的。
// 注意:没有等效的 `componentWillReceiveState` 。传入的道具转换可能会导致状态改变,但情况恰恰相反。如果你需要它,你可能正在寻找 `componentWillUpdate` 。
componentWillReceiveProps: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_MANY,
// 在决定是否应该因接收新的道具和状态而更新组件时调用。 当您确定转换到新的道具和状态不需要更新组件时,可以将此作为 `return false` 的机会。
shouldComponentUpdate: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_ONCE,
// 由于从 `this.props` 和 `this.state` 转换为 `nextProps` 和 `nextState` 而导致组件即将更新时调用。使用此作为在更新发生之前执行准备的机会。
// 注意:您**不能**在此方法中使用 `this.setState()` 。
componentWillUpdate: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_MANY,
// 更新组件的DOM表示时调用。 将此作为在更新组件时对DOM进行操作的机会。
componentDidUpdate: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_MANY,
// 当组件即将从其父组件中删除并销毁其DOM表示时调用。 使用此作为释放任何外部资源的机会。 注意:没有 `componentDidUnmount` ,因为您的组件将被该点销毁。
componentWillUnmount: SpecPolicy.DEFINE_MANY,
// 到此
updateComponent: SpecPolicy.OVERRIDE_BASE
};生命周期图
来看一下生命周期图:
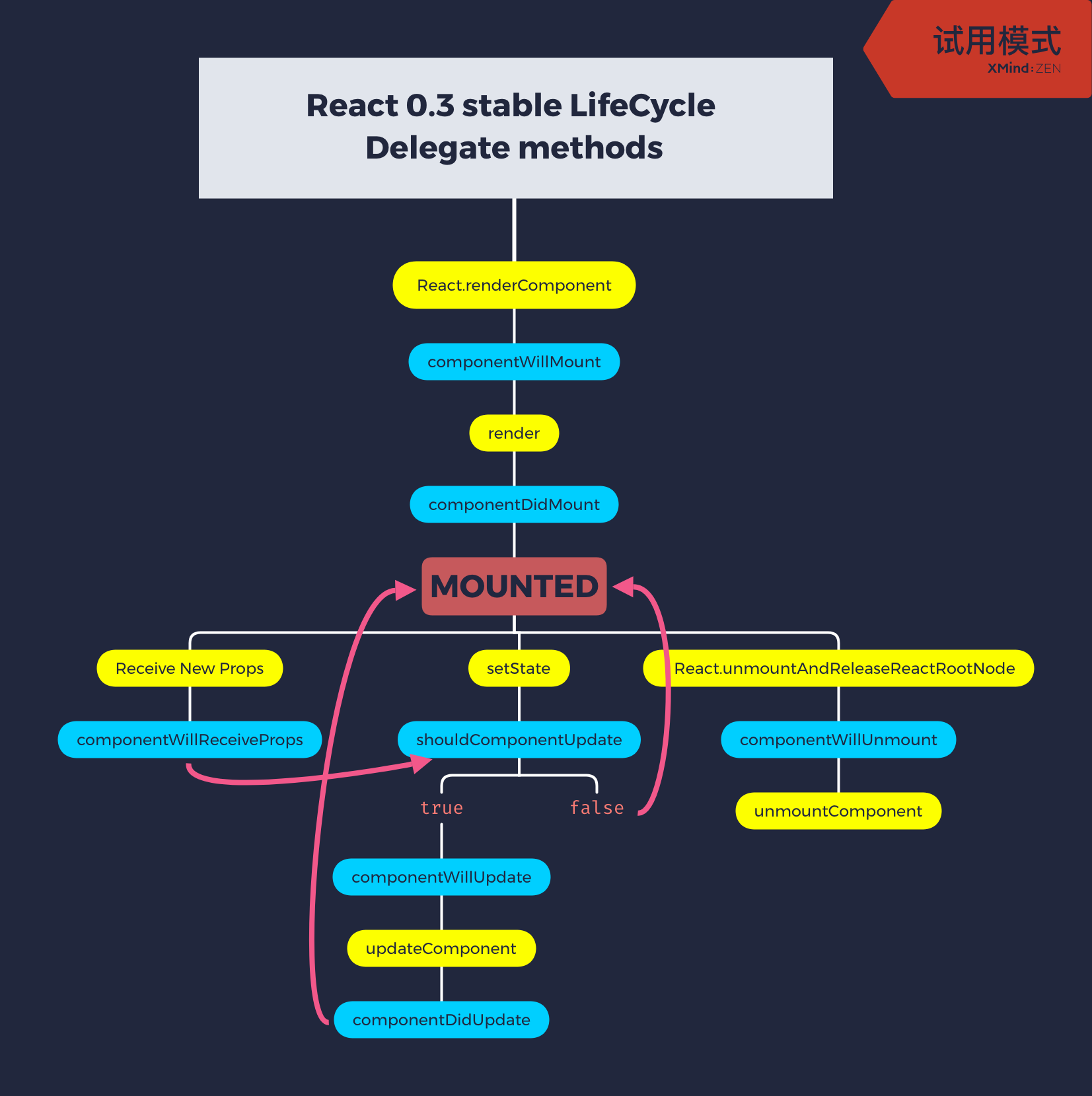
- 本文链接: https://zongzi531.github.io/2019/04/07/LSC-React-07/
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 许可协议。转载请注明出处!